
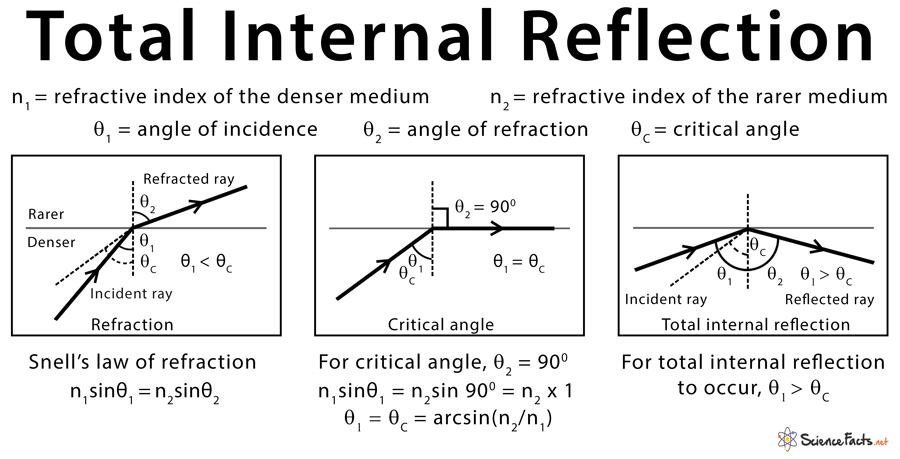
In such a phenomenon, some portion of the light gets reflected back into the same medium and another portion of the incident light gets refracted into the different medium. When a light beam or ray travels from an optically denser medium to a rarer medium or less optically denser medium, internal reflection occurs. Thus this extreme value is known as critical value and that angle is known as the critical angle.Internal reflection is a part of optics that explains the concept of travelling of light. And all those rays that incident at an angle greater than this particular value will get reflected. The answer to this is that all those rays that incident with an angle less than this angle gets refracted and reach another medium. Now, the question arises why it was named so? Due to which complete reflection is noticed in it without major losses.Ĭritical angle plays a crucial role in TIR. As diamond has a lower value of critical angle and has a higher refractive index.
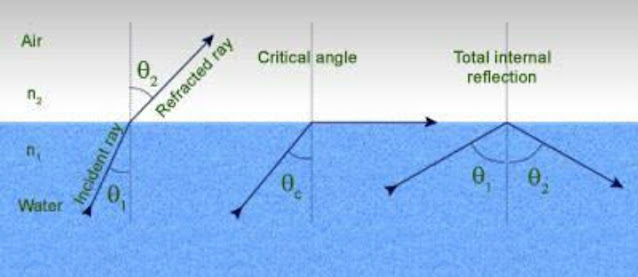
This phenomenon is majorly experienced on sunny days. In a mirage, due to refraction of light water illusion is noticed because of the non-uniform medium.
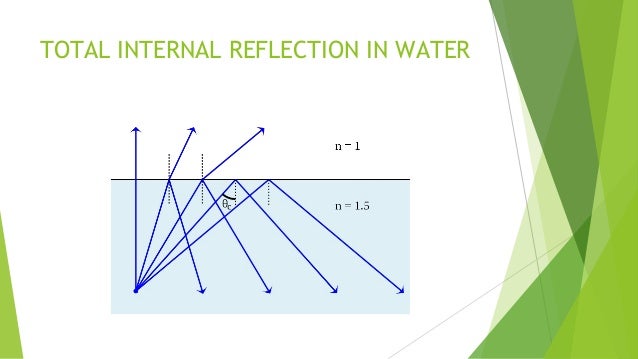
So, we can see, that ray 4 on striking the medium that is making an angle i 4, now gets reflected towards the same medium through which it was incident. This is represented by ray 4 in the above figure. The advancement is nothing but it is simply that now the ray strikes the surface with an angle more than the critical angle. Now, let us have a look at the advancement of the figure that is shown above: So, refraction is nothing but the bending of light rays while moving from a medium to another. Then that specific angle of incidence is known as the critical angle. The angle of incidence for which the refracted ray makes an angle of 90° and starts moving along the surface. Thus, this case shows the refraction angle is 90°. So, in this case, the refracted ray moves along the surface. So, after striking the surface, ray 2 gets refracted by making an angle r 2 in the rarer medium.Ĭonsider another case when the angle of incidence is increased further, this is represented by ray 3. Further, we can see, that ray 2, incidents the surface with some greater angle than the previous. Here, the angle of the refracted ray is represented by r 1.
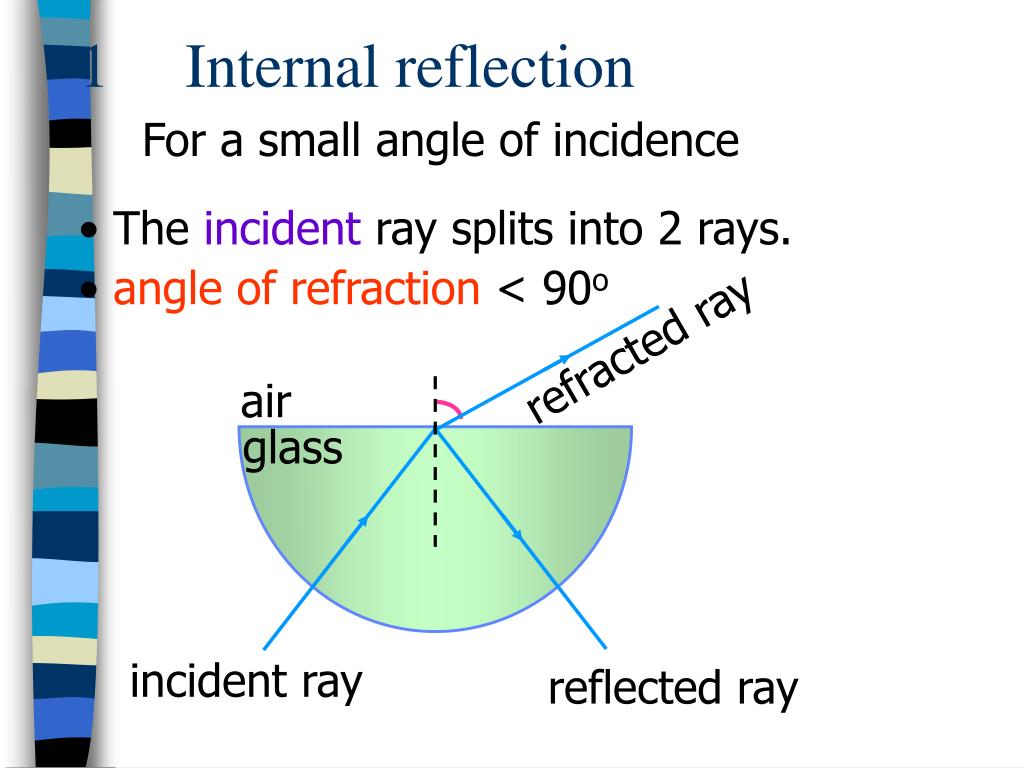
So, after striking the surface the ray gets refracted and reaches a rarer medium. In the above figure, ray 1 represents some specific angle of incidence.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
